基础知识
理解sda与sdb
ll /dev/sd*
<<'COMMENT'
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 0 5月 10 10:32 /dev/sda
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 1 5月 10 10:32 /dev/sda1
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 2 5月 10 10:32 /dev/sda2
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 5 5月 10 10:32 /dev/sda5
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 16 5月 10 10:43 /dev/sdb
brw-rw---- 1 root disk 8, 17 5月 10 10:39 /dev/sdb1
COMMENT
Linux系统检测到有两块物理硬盘,其中sda为SATA第一接口连接的硬盘,sdb为SATA第二接口连接的硬盘。而sda1,sda2和sd5分别表示sda硬盘的两个分区。
SATA(Serial Advanced Technology Attachment)
-
高技术配置(Advanced Technology Attachment,简称“ATA”)与由集成驱动电子设备(Integrated Drive Electronics,简称IDE)技术实现的磁盘驱动器关系最密切。
-
IDE是一种计算机系统接口,主要用于硬盘和CD-ROM,本意为“把控制器与盘体集成在一起的硬盘”。现在PC机使用的硬盘,大多数都是IDE兼容的,只需用一根电缆将它们与主板或适配器连起来就可以了。
-
一般说来,ATA是一个控制器技术,而IDE是一个匹配它的磁盘驱动器技术,但是两个术语经常可以互用。ATA是一个花费低而性能适中的接口,主要是针对台式机而设计的,今天销售的大多数ATA控制器和IDE磁盘都是更高版本的,称为ATA-2和ATA-3,与之匹配的磁盘驱动器称为增强的IDE (Eide)。
-
把盘体与控制器集成在一起的做法,减少了硬盘接口的电缆数目与长度,数据传输的可靠性得到了增强,硬盘制造起来变得更容易,因为厂商不需要再担心自己的硬盘是否与其他厂商生产的控制器兼容,对用户而言,硬盘安装起来也更为方便。
-
ATA是用传统的40-pin并行数据线连接主板与硬盘的,外部接口速度最大为133MB/s,因为并行线的抗干扰性太差,且排线占空间,不利电脑散热,将逐渐被SATA所取代。ATA主机控制器芯片差不多集成到每一个生产的系统板,提供连接4个设备的能力。ATA控制器已经变得非常廉价和常见,致使购买一块没有ATA接口的PC主板是很难的,
-
但在SATA技术日益发展下,没有ATA的主版已经出现,而且Intel在新型的芯片组中已经不默认支持ATA接口,主机版厂商需要另加芯片去对ATA作出支持(通常是为了兼容旧有硬盘和光盘驱动器)
LVM(Logical Volume Manager)
逻辑卷管理 (LVM)相较于传统的分区管理有许多优点,已经成为大多数Linux发行版安装时的默认选择。LVM最大的优点应该是能方便的按照你的意愿调整(减小或增大)逻辑分区的大小。
-
LVM的组成结构:
把一块或多块硬盘或者一个或多个分区配置成物理卷(PV, Phsical Volume)。
一个用一个或多个物理卷创建出的卷组(VG, Volume Group)。可以把一个卷组想象成一个单独的存储单元。 在一个卷组上可以创建多个逻辑卷。每个逻辑卷相当于一个传统意义上的分区——优点是它的大小可以根据需求重新调整大小。
-
PV(Phsical Volume,物理卷),PV是VG的组成部分,有分区构成,多块盘的时候,可以把一块盘格式化成一个主分区,然后用这个分区做成一个PV,只有一块盘的时候,可以这块盘的某一个分区做成一个PV,实际上一个PV就一个分区
-
VG(Volume Group, 卷组),有若干个PV组成,作用就是将PV组成到以前,然后再重新划分空间
-
LV(Logical Volume,逻辑卷),LV就是从VG中划分出来的卷,LV的使用要比PV灵活的多,可以在空间不够的情况下,增加空间
硬盘分区
man/help文档
fdisk /dev/sdb
<<'COMMENT'
Command (m for help): m
Command action
a toggle a bootable flag
b edit bsd disklabel
c toggle the dos compatibility flag
d delete a partition
l list known partition types
m print this menu
n add a new partition
o create a new empty DOS partition table
p print the partition table
q quit without saving changes
s create a new empty Sun disklabel
t change a partition's system id
u change display/entry units
v verify the partition table
w write table to disk and exit
x extra functionality (experts only)
COMMENT
查看硬盘信息
fdisk -l
<<'COMMENT'
Disk /dev/sda: 500.1 GB, 500107862016 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 60801 cylinders, total 976773168 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 4096 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 4096 bytes / 4096 bytes
Disk identifier: 0x000c2310
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sda1 * 2048 960620543 480309248 83 Linux
/dev/sda2 960622590 976771071 8074241 5 Extended
Partition 2 does not start on physical sector boundary.
/dev/sda5 960622592 976771071 8074240 82 Linux swap / Solaris
Disk /dev/sdb: 16.2 GB, 16231956480 bytes
255 heads, 63 sectors/track, 1973 cylinders, total 31703040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xc3072e18
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
/dev/sdb1 112 31703039 15851464 c W95 FAT32 (LBA)
COMMENT
删除已有硬盘分区
fdisk /dev/sdb
<<'COMMENT'
Command (m for help): d
Selected partition 1
Command (m for help): d
No partition is defined yet!
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
COMMENT
fdisk -l
<<'COMMENT'
...
Disk /dev/sdb: 16.2 GB, 16231956480 bytes
64 heads, 32 sectors/track, 15480 cylinders, total 31703040 sectors
Units = sectors of 1 * 512 = 512 bytes
Sector size (logical/physical): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
I/O size (minimum/optimal): 512 bytes / 512 bytes
Disk identifier: 0xc3072e18
Device Boot Start End Blocks Id System
COMMENT
- 选择d:删除分区
- 选择w:保存
硬盘分区
fdisk /dev/sdb
<<'COMMENT'
Command (m for help): n
Partition type:
p primary (0 primary, 0 extended, 4 free)
e extended
Select (default p): p
Partition number (1-4, default 1): 1
First sector (2048-31703039, default 2048):
Using default value 2048
Last sector, +sectors or +size{K,M,G} (2048-31703039, default 31703039):
Using default value 31703039
Command (m for help): w
The partition table has been altered!
Calling ioctl() to re-read partition table.
Syncing disks.
COMMENT
- 选择n:创建分区
- 选择p:主分区
- 选择e:逻辑分区
- Partition number:分区个数。这里选择分为一个区
- First sector:第一块扇区号。这里以2048为开始
- With the death of the legacy BIOS (ok, its not quite dead yet) and its replacement with EFI BIOS, a special boot partitionis needed to allow EFI systems to boot in EFI mode. Starting the first partition at sector 2048 leaves 1Mb for the EFI boot code. Modern partitioning tools do this anyway and fdisk has been updated to follow suit. 大意为,由于EFI的兴起,要给EFI 代码留磁盘最开始的1M空间
- Last sector:最后一块扇区号。这里默认代表全部的扇区,也可以制定大小,例如
+1024m,即分出1G空间 - 选择w:保存退出
分区格式化
mkfs -t ext4 /dev/sdb1
<<'COMMENT'
mke2fs 1.42.9 (4-Feb-2014)
Filesystem label=
OS type: Linux
Block size=4096 (log=2)
Fragment size=4096 (log=2)
Stride=0 blocks, Stripe width=0 blocks
991232 inodes, 3962624 blocks
198131 blocks (5.00%) reserved for the super user
First data block=0
Maximum filesystem blocks=4060086272
121 block groups
32768 blocks per group, 32768 fragments per group
8192 inodes per group
Superblock backups stored on blocks:
32768, 98304, 163840, 229376, 294912, 819200, 884736, 1605632, 2654208
Allocating group tables: done
Writing inode tables: done
Creating journal (32768 blocks): done
COMMENT
格式化完成,便可以进行硬盘的挂载
硬盘合并
在生产中使用过,但是没有留下记录。所以这里只有命令,没有显示出来的COMMENT
安装
# centos
sudo yum install lvm2
# ubuntu
sudo apt-get install lvm2
目标硬盘
- 硬盘1
/dev/sdb - 硬盘2
/dev/sdc
创建物理卷PV
pvcreate /dev/sdb
pvcreate /dev/sdc
创建卷组VG
# vgcreate [自定义LVM名称] [设备]
vgcreate LVM /dev/sdb
扩展卷组VG
# vgextend [自定义vg名称] [设备]
vgextend LVM /dev/sdc
创建逻辑卷LV
# lvcreate -L [自定义分区大小] -n [自定义分区名称] [vg名称]
# *分区大小不能超过硬盘容量总和*
lvcreate -L 5.0T -n DB_DATA LVM
分区格式化
mkfs -t ext4 /dev/LVM/DB_DATA
挂载
mount /dev/LVM/DB_DATA /mnt
硬盘挂载
挂载
mount /dev/sdb1 /mnt
df
<<'COMMENT'
Filesystem 1K-blocks Used Available Use% Mounted on
udev 3922192 4 3922188 1% /dev
tmpfs 786724 1300 785424 1% /run
/dev/sda1 472640776 220337520 228271412 50% /
none 4 0 4 0% /sys/fs/cgroup
none 5120 0 5120 0% /run/lock
none 3933604 76 3933528 1% /run/shm
none 102400 64 102336 1% /run/user
/dev/sdb1 15470568 38704 14622956 1% /mnt
COMMENT
可以看到硬盘已经挂载到/mnt路径下
重启自动挂载
echo "/dev/sdb1 /mnt ext4 defaults 1 2" >> /etc/fstab
- /dev/sdb1: 目标分区
- /mnt: 挂载路径
- ext4: 分区格式
- defaults:挂载时所要设定的参数(只读,读写,启用quota等),输入defaults包括的参数有(rw、dev、exec、auto、nouser、async)
- 1: 使用dump是否要记录,0是不要
- 2: 开机时检查的顺序,是boot系统文件就为1,其他文件系统都为2,如不要检查就为0
Mac上的硬盘挂载
获取硬盘信息
diskutil list
<<'COMMENT'
/dev/disk0 (internal, physical):
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: GUID_partition_scheme *500.3 GB disk0
1: EFI EFI 209.7 MB disk0s1
2: Apple_CoreStorage Macintosh HD 499.4 GB disk0s2
3: Apple_Boot Recovery HD 650.0 MB disk0s3
/dev/disk1 (internal, virtual):
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: Apple_HFS Macintosh HD +499.1 GB disk1
Logical Volume on disk0s2
12E6ECD1-780D-428C-94A4-500CA2054F2C
Unlocked Encrypted
/dev/disk2 (disk image):
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: MATLAB_R2016A +7.7 GB disk2
/dev/disk3 (external, physical):
#: TYPE NAME SIZE IDENTIFIER
0: FDisk_partition_scheme *15.7 GB disk3
1: Apple_HFS yhy 15.7 GB disk3s1
COMMENT
- 可以看到类型为
Apple_HFS的名为yhy的ID为disk3s1,该硬盘默认路径为/Volumes/下面
获取硬盘的UUID
diskutil info /Volumes/yhy
<<'COMMENT'
Device Identifier: disk3s1
Device Node: /dev/disk3s1
Whole: No
Part of Whole: disk3
Volume Name: yhy
Mounted: Yes
Mount Point: /Volumes/yhy
Partition Type: Apple_HFS
File System Personality: Journaled HFS+
Type (Bundle): hfs
Name (User Visible): Mac OS Extended (Journaled)
Journal: Journal size 8192 KB at offset 0x78000
Owners: Disabled
OS Can Be Installed: No
Media Type: Generic
Protocol: USB
SMART Status: Not Supported
Volume UUID: A35BB405-4443-372B-9889-AA73D680D985
Disk Size: 15.7 GB (15720250368 Bytes) (exactly 30703614 512-Byte-Units)
Device Block Size: 512 Bytes
Volume Total Space: 15.7 GB (15720247296 Bytes) (exactly 30703608 512-Byte-Units)
Volume Used Space: 40.5 MB (40521728 Bytes) (exactly 79144 512-Byte-Units) (0.3%)
Volume Available Space: 15.7 GB (15679725568 Bytes) (exactly 30624464 512-Byte-Units) (99.7%)
Allocation Block Size: 4096 Bytes
Read-Only Media: No
Read-Only Volume: No
Device Location: External
Removable Media: Removable
Media Removal: Software-Activated
COMMENT
- 可以得知
UUID=A35BB405-4443-372B-9889-AA73D680D985
写入fstab文件
echo "UUID=A35BB405-4443-372B-9889-AA73D680D985 /tmp hfs auto" >> /etc/fstab
/etc/fstab在默认初始环境中不存在的
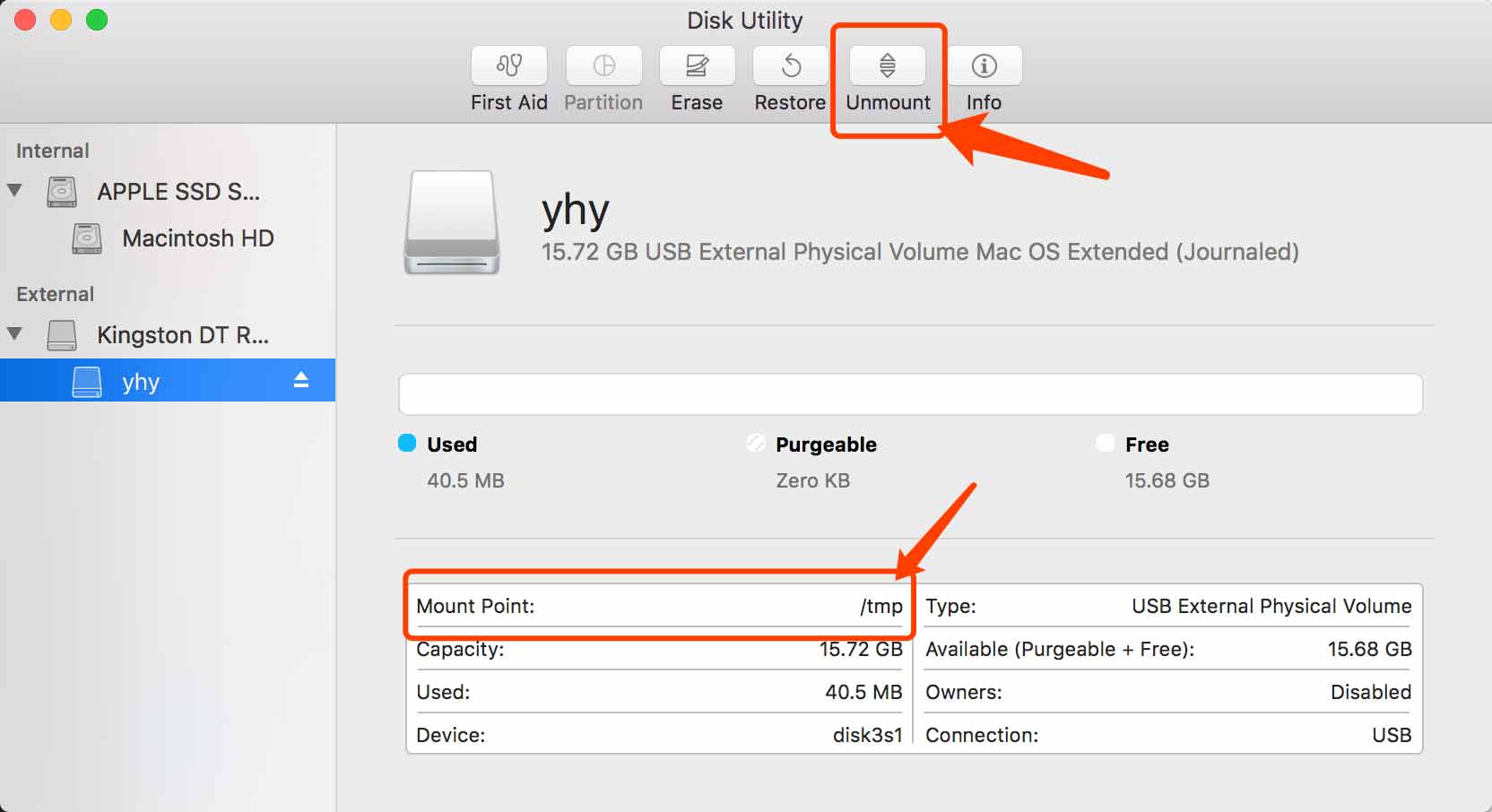
Disk-Utility工具
在Mac上有硬盘工具(Disk Utility),在其中可以查看硬盘信息
点击Unmount,再点Mount,则可以看到硬盘yhy已挂载载/tmp上
参考博文
- Linux下添加新硬盘,分区及挂载
- 为什么Linux的fdisk分区时第一块磁盘分区的First Sector是2048
- linux 硬盘分区,分区,删除分区,格式化,挂载,卸载笔记
- Linux硬盘合并
- pvcreate命令
- pv,vg和lv的概念
- mac设置自动挂载分区到指定路径
- Mac下用一个单独的磁盘分区作为/Users的挂载点
 本作品由陈健采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。
本作品由陈健采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。